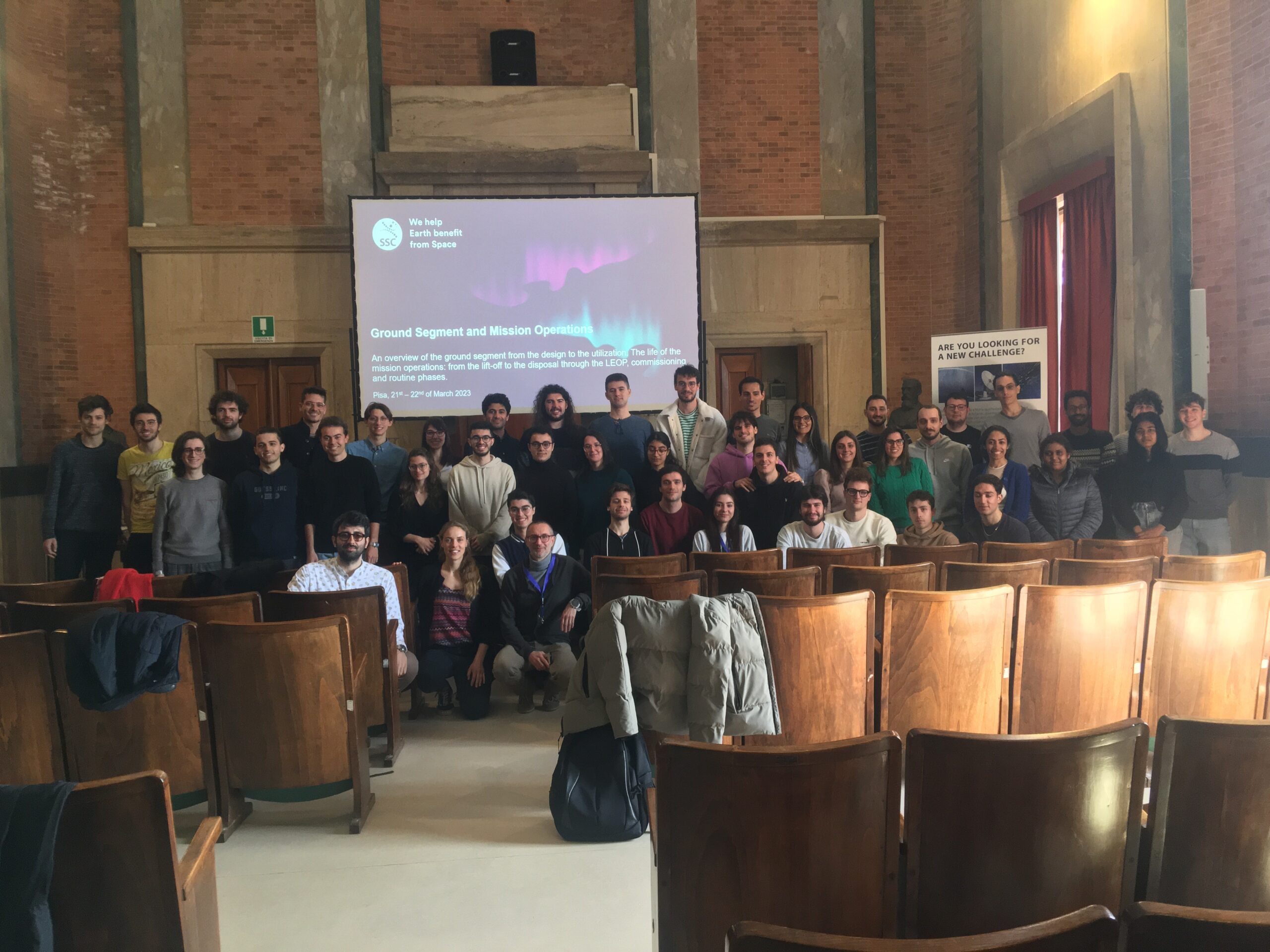
SSC Workshop at Pisa University
22nd March 2023
Welcome Domenico to the Recruitment Team
15th May 2023The European Space Agency’s (ESA) Jupiter Icy Moons Explorer (JUICE) mission has taken a significant step forward with the successful launch of its spacecraft. The mission was launched on an Ariane 5 rocket from Kourou in French Guiana on April 14, 2023. JUICE is a crucial mission in exploring the Jupiter system, with a focus on the icy moons Ganymede, Europa, and Callisto.
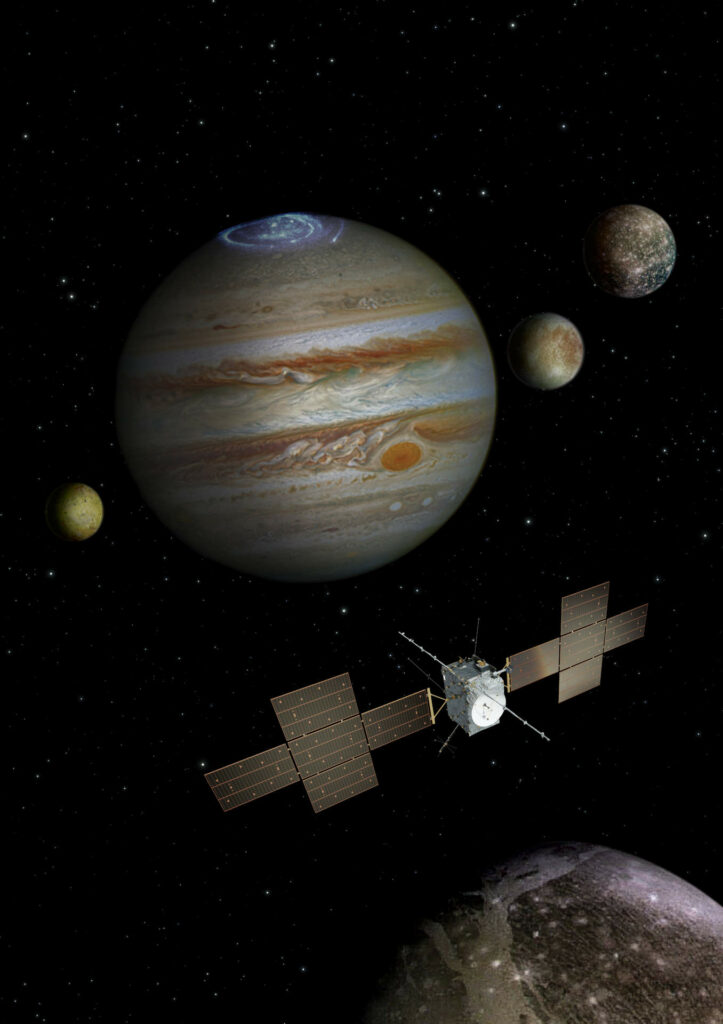

The JUICE mission will provide new insights into the composition, geology, and potentially habitable environments of these icy moons. The spacecraft will study Jupiter’s magnetic environment and the interactions between the giant planet and its moons, which will help to answer questions about the formation and evolution of the solar system.
Aurora Technology‘s excellent team of scientists and engineers plays a fundamental role in the JUICE mission, particularly in the science operations of JUICE payload systems.
The JUICE mission is a joint project between ESA and its international partners, including NASA and the Japanese Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA). The mission has been in development for several years, and the launch marks a significant milestone in its progress.
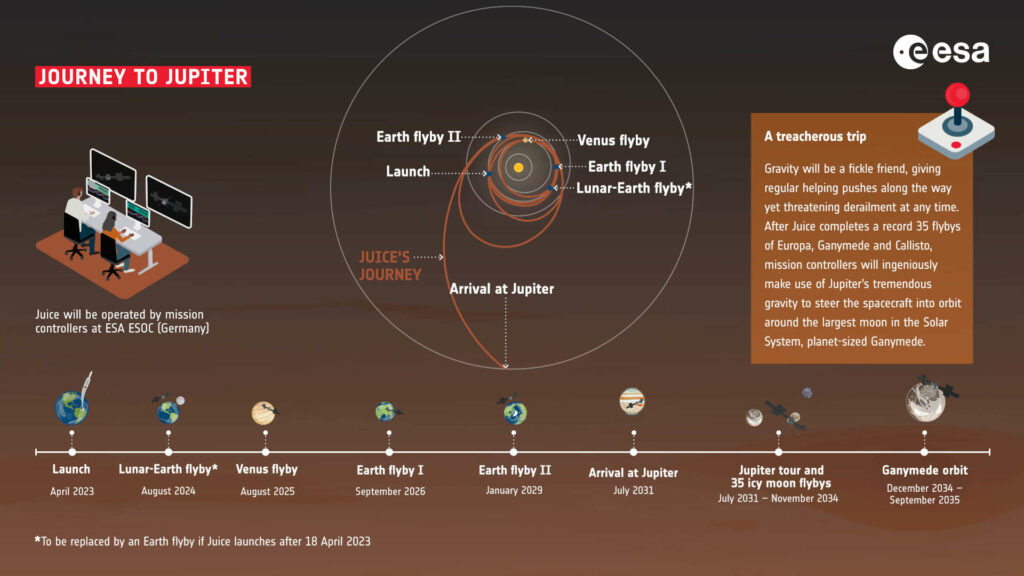
The spacecraft is expected to reach Jupiter in 2031 (but its science mission will begin around six months before entering orbit around the giant planet), where it will spend at least three years studying the giant planet and its moons. JUICE will use a combination of remote sensing and in-situ measurements to provide a comprehensive understanding of the Jupiter system and its potential for supporting life.
In conclusion, the successful launch of the JUICE spacecraft marks a significant milestone in the exploration of the Jupiter system. We are extremely proud that Aurora Technology‘s contribution to the mission’s science operations plays a crucial role in advancing the understanding of our solar system.

